Case Study of SAS Business Strategy
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 2181 words | ✓ Published: 10 May 2021 |
- What type of strategy (cost leadership/differentiation) does SAS take? Discuss in terms of personnel, resources and activities performed. Provide a thorough analysis to justify your answer.
SAS undertakes a Porter Force model of differentiation strategy which allows them to offer a uniqueness compared to other competitors. This strategy focuses on competitive advantage as SAS’s key focus. One way they have done this is by shifting to cloud base technology. SAS produces innovative products that offer high-quality software. They market it as suitable for every customer due to the enhanced simplicity of decision making provided. The product must fit current market demand and provide their customers incentive to return.
One way that SAS seeks to gain competitive advantage is through their constant reinvestment in R&D. They aim to stay ahead of the game in technology all the while bringing immense satisfaction to their customer base. SAS is considered a leading influence in the world of analytics and it is important for them to retain this unique position in the market. Technology is growing every day and continual investment is required for companies to stay ahead of the curve, hence the large amount of funds. This is another proof that SAS is a differentiator because if they were cost driven, expenses would be kept to a minimum.
Another way SAS gains competitive advantage as a differentiator is through the fostering of a positive work environment for employees. SAS shows faith in their employees by providing them challenging opportunities to work through. They also respect the individuals’ need for a life outside of work, provided they meet the 8-hour day standard. SAS aims to reduce the employees’ stress in providing core benefits such as: health care, gym, day-care and rewards for employees that demonstrate good performance. These working conditions help employees balance both personal and professional needs that are vital for a promoting a positive workplace. Once again, this requires a large investment of funds proving that low-cost methods are not as important as standing out.
SAS is a unique and powerful brand which currently stands out from their competitors. They are willing to spend money to improve and create value in their business. This is seen in their investment in staff, business growth and development opportunities.
- What measures or key success factors would you consider important to evaluate the performance of SAS? Provide examples of at least three key success factors.
As discussed in the previous question, SAS is a differentiator focused on quality and customer retention. Based on this, we have identified the following key success factors which are integral to the business:
- Customer satisfaction – Customer satisfaction is incredibly important to SAS and the analytics industry in general. The systems SAS develop aim to make people’s lives simpler and easier. If they do not follow through on this, their business will not be successful at all, therefore they need to keep up to speed with customer needs and demands.
- Technological advancements. The most obvious KSF would be the technological capabilities. The work SAS does to provide a service for their customers is fully based on their tech capabilities and information available.
- Product quality. SAS must focus on what makes their product unique and more valuable to their customers than that of their competitors. The product is only going to be more valuable if it is quality thereby making quality a top KSF.
- Buyer loyalty. Loyal customers are important in this industry. Customers do not want to continually be shopping around for analytics products as it is a time-consuming process. The more customers SAS can attract and retain, the better it is for the company. Customers will not be loyal if the product is bad which reinforces the importance of product quality above.
- Brand image. SAS has a good reputation in the market and make every effort to prolong that image. The more customers they retain with their high-end product, the better the brand image they will retain. This reinforces the need for all products to meet the highest quality as it does not take much to ruin a business name!
The key success factors for SAS are directly related to their strategy. The high customer focus and rapidly changing tech market are the main challenges for the company which if they can master, will prolong their success for many years to come.
- You are a consultant for SAS. Discuss the possible problems of profit planning at SAS, based on the current strategies. How could you address these problems by focusing on the interconnected strategic budgeting cycles? Provide a thorough analysis to justify your answer.
Profit planning is a series of actions that are implemented to achieve a targeted profit level. This work is important as it can help provide decisions on improvements to cost efficiency and can allow resources to be invested or reduce costs.
Potential profit problems at SAS I have identified include:
- There have been constant changes in strategy when SAS began to adjust their “pricing strategy to smooth multi-year revenue pricing more evenly over contract periods.” This was done where they reported a relatively flat revenue (0.5%) in 2019 after they had adopted a new accounting standard
- Investments in Research and development may not always return a profit. SAS have substantial investment in software innovation, education, and expert services with $1 billion invested over 3 years. In addition, they continue to reinvest in R&D an average of 25% of revenue. This significant spending can be of risk to the organisation if it does not return profit as it may result in cash flow issues in the short term.
- SAS maintains employee satisfaction by using a significant amount of revenue and time. While this has a clear positive with a 4% turnover rate (opposes to a 20% turnover rate within the industry) the money and time spent may need to be re-evaluated in the future.
- SAS partners had a direct impact on over half of their new sales (56%) with half of their top 50 deals. This is a potential issue as it appears that SAS is relying on their partners for a large proportion of their sales rather than the management employed.
Interconnected strategic budgeting cycles; There are three aspects of interconnected strategic budgeting cycles can be utilized: the cash cycle (operating cash), the income cycle (revenue/ profit) and the asset cycle (asset utilization).
- Due to a shift in in the recording standard at one point, SAS recorded flat growth at 5%. This does not necessarily represent the accurate growth of the company, however. Thus, an estimation of predicted sales is important and what growth those sales represent. This can be done by managing trends on a month to month or year to year basis which is recognized as step one in the income cycle.
- Interconnected strategic budgeting cycles can also be applied when deciding the appropriate amount to spend on investments. As previously mentioned, there are three stages to this process in which the organisation’s overall spending and income can be adequately assessed. Methods applied within this strategy may include comparing the return on investment (ROI) to assess the efficiency of an investment made. A high ROI will mean that the investments returned a favourable profit and provides insight into whether the project is worth continuing/repeating in the future.
- Employee satisfaction plays a big role in the organisation’s effectiveness and efficiency. However, with the significant amount of money and time invested into employees, the organisation must ensure that these “committed costs” under fixed (non-variable) costs do not impact other spending necessities including discretionary costs (advertising) or activity based indirect costs (set up and supervision costs). Overinvestment into employees’ enjoyment may also distract them from the tasks at hand!
- While it is a positive for the business to gain new sales, half of the “new” sales come from partners which can cause issues in the future for instance if a partnered organisation separates or collapses. Forecasting and planning on their own managerial level needs some focus so they also can align within the wider business model. Forecasting analyses the varying costs and cost behaviour associated with operating expenses. What is the monetary amount provided to partnered businesses, and the return on this spending? It is no doubt that SAS needs to work on obtaining sales on their own as half of the top 50 sales were influenced by their partners.
- Suggest what is the type of corporate structure should be used in SAS? Explain why SAS should use this structure. (Hint: connect to its current strategy)
As established above, SAS is a differentiator and their key success factors relate largely to customer satisfaction. Because of this, SAS would benefit most from a structure that incorporates market-based work units. Market-based work units are essentially groups/teams of people working on one specific output (product). Within each work unit, all functions relating to their output are performed. This includes all processes from design to sales, meaning all the functions are tailored specifically to every product. Employees should be organized into the various work units according to their output.
The reason I believe that market-based work units would be most effective is their direct relationship to customer focus. Because the work units are dedicated to one output only, management will have a better idea of the market they are reaching and not just the numbers sitting in front of them. Managers also have access to real-time information meaning they can adapt to any market changes much sooner than they otherwise could. SAS are very customer focused and invest much of their profit back into research and development for their customers. Technological advancement is a big part of product differentiation are their competitive advantage in the analytics market meaning they need to understand their customers even more!
The corporate structure of SAS also seems quite decentralized. Employees are empowered to share their ideas and developments and are provided with many challenging projects. There is a large focus on productivity and ingenuity of individuals without a ‘top-down’ hierarchy in place. Such decentralization also increases managerial motivation while also placing greater responsibility on those manager’s shoulders. Decentralized management of market-based work units is not without its challenges, however. Not only is management more complex, but they must deal with inherent competition that arises between work units. Decentralization can be difficult to manage on its own as creativity and ingenuity needs to be harnessed for the right reasons and appropriate focus on business goals needs to be ensured. Managers must encourage the sharing of relevant information between different work units and always remember they are part of a company, not just an individual unit.
Overall, the decentralized market-based work unit structure benefits SAS well as it fits with their strategy as well as their work ethic. Decentralization ensures their employees feel valued and needed while the individual units are easily able to understand their customer base.
- Where does the financial department fit within SAS’s structure as you describe above? In your response, explain what type of responsibility centre SAS’s financial department would be classified as? Provide two performance measures that can be used in the responsibility centre you identified.
SAS is a company that develops and markets an analytics software helping their customers access, manage, analyse, and report on data to aid in decision-making. Their financial department focuses on the overall profits or costs required to run the company and determines the amount to invest in research and development. SAS’s financial department would be classified as an investment division (investment centre). An investment centre is a responsibility centre containing revenue, expenses, and an appropriate investment base. The responsibility centres are often separated from one another by location, type of product, functions, and necessary management skills. In this case, as discussed in the previous question, SAS’s market-based work units focus on individual technology and processes unique to each product. This includes all processes from their development stage to manufacturing, to the customer’s interface. The financial department of SAS is positioned just under senior management above the individual work units as seen below (Figure 1).
Investment centres have one key method which evaluates financial performance. This is termed Return on Investment (ROI). ROI is essentially a measure of probability. SAS calculates ROI separately for each different technology represented by each work unit segment. In 2019, SAS committed $1 billion in AI which resulted in optimized ROI on AI projects. Separating ROI provides extra benefit to the company because it shows a comparison between the products. This information is used to examine which products need more attention. Another investment centre evaluation method is Residual Income (RI). RI is the amount of operating profit remaining after SAS has paid all costs of capital used to generate those revenues. Residual Income evaluates investments by applying a common cost of capital rate to all products of SAS. SAS should always remember, however, that investing in an individual product which may benefit one department should be viewed in conjunction with the benefit to the entire organization. This way management will always have a bigger focus!
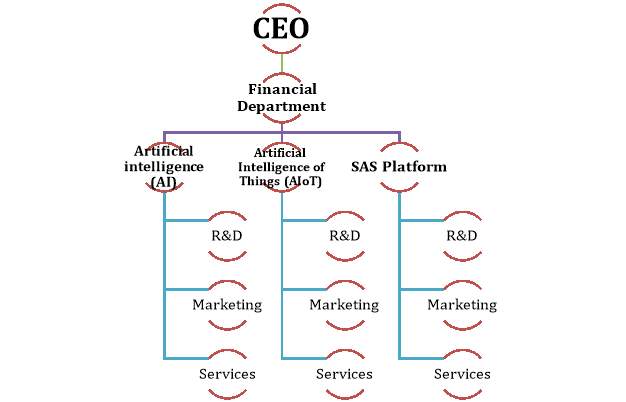
Figure 1: A draft of SAS’s market-based work units’ structure
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


